NIEHS researchers have discovered a therapy that targets host cells rather than bacterial cells in treating bacterial pneumonia in rodents. The method involves white blood cells of the immune system called macrophages that eat bacteria, and a group of compounds that are naturally produced in mice and humans called epoxyeicosatrienoic acids (EETs). The research was published in the Journal of Clinical Investigation.
 Edin said EETs are a subset of fatty molecules the body makes called eicosanoids. (Photo courtesy of Steve McCaw / NIEHS)
Edin said EETs are a subset of fatty molecules the body makes called eicosanoids. (Photo courtesy of Steve McCaw / NIEHS)According to the World Health Organization, pneumonia caused by Streptococcus pneumoniae, or pneumococcal pneumonia, is the leading cause of pneumonia deaths worldwide each year. Although physicians usually prescribe antibiotics to treat this severe lung infection, treatment is not always successful, and in some cases, the bacteria become resistant.
Matthew Edin, Ph.D., a staff scientist in the NIEHS Environmental Cardiopulmonary Disease Group, wanted to find a way to augment the body’s immune system to resolve the infection.
The role of EETs
To keep tissues healthy, EETs work to limit inflammation, but during infections caused by S. pneumoniae and other microorganisms, inflammation ramps up after lung cells induce certain substances that prompt macrophages to gobble up the bacteria. Edin and colleagues found that one way to get macrophages to eat more bacteria is to decrease the ability of EETs to do what they normally do, which is limit inflammation.
Edin led the team that found infection induces a protein called soluble epoxide hydrolase (sEH), whiich degrades EETs. In contrast, when sEH is blocked, EET levels skyrocket, hampering the macrophages’ ability to sense and eat bacteria. As a result, the bacteria continue to reproduce in the lung, which leads to severe lung infection and death.
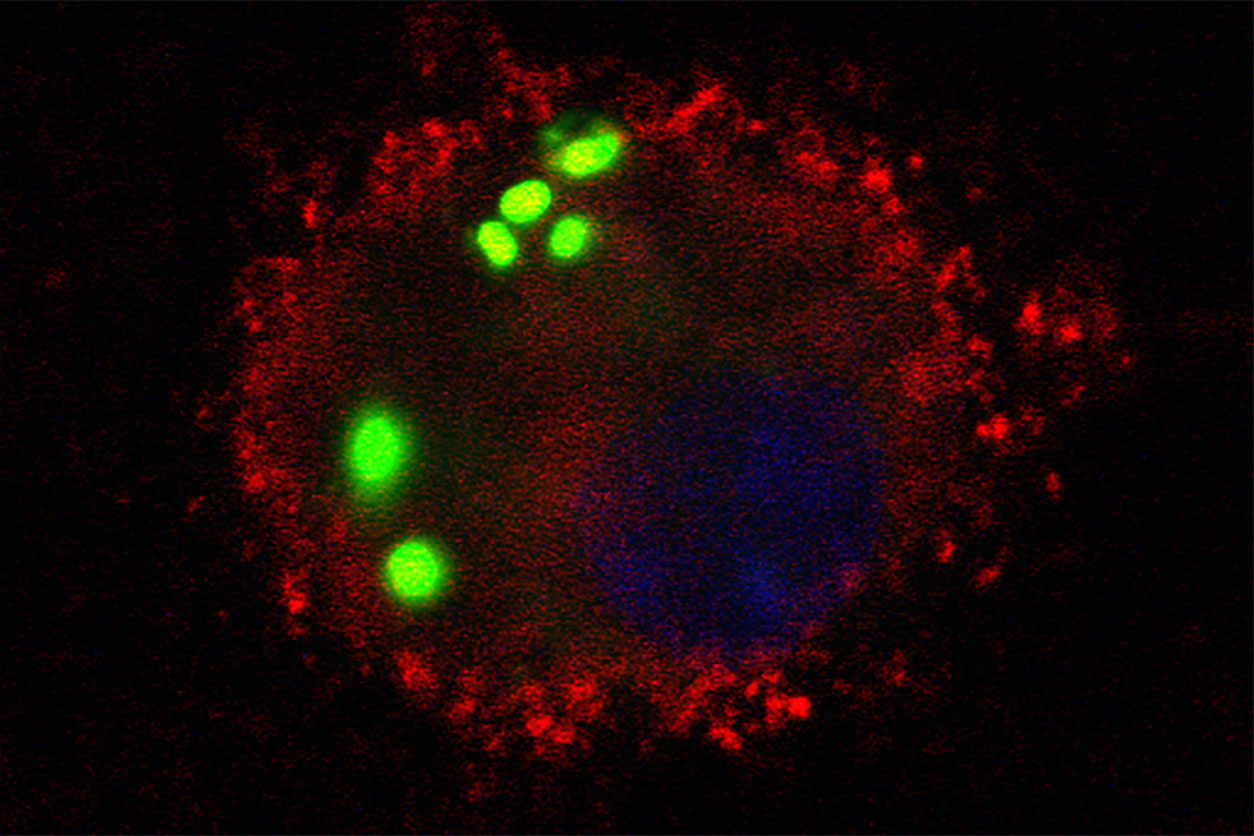 The image shows S. pneumoniae bacteria, shown in green, that have been engulfed by a macrophage from a wild-type mouse. (Image courtesy of Hong Li / NIEHS)
The image shows S. pneumoniae bacteria, shown in green, that have been engulfed by a macrophage from a wild-type mouse. (Image courtesy of Hong Li / NIEHS)Compounds that block EETs
At the other end of the spectrum, blocking EETs using a synthetic molecule called EEZE boosted the eating capacity of the macrophages, leading to reduced numbers of bacteria in the lungs of mice. The scientists saw the same result when they placed bacteria and macrophages harvested from lung and blood samples of human volunteers in test tubes at the NIEHS Clinical Research Unit.
 In addition to his role as NIEHS Scientific Director, Zeldin leads the NIEHS Environmental Cardiopulmonary Disease Group. (Photo courtesy of Steve McCaw / NIEHS)
In addition to his role as NIEHS Scientific Director, Zeldin leads the NIEHS Environmental Cardiopulmonary Disease Group. (Photo courtesy of Steve McCaw / NIEHS)'EEZE is safe and effective in mice, but scientists could develop similar compounds to give to humans,' said Edin, who is co-lead author of the paper. 'These new molecules could be used in an inhaler or pill to promote bacterial killing and make the antibiotics more effective.'
Physiological impacts
NIEHS Scientific Director Darryl Zeldin, M.D., corresponding author of the research, has spent several years studying EETs and their impact on the human body. He and his research group determined that EETs provide beneficial cardiovascular effects, such as lowering blood pressure and inflammation, and improving cell survival after a stroke or heart attack. He stressed, however, that the involvement of EETs in the process of inflammation can be good or bad depending on the context.
'EETs can suppress the inflammatory response, which is good, but if they block it too much, they’re going to make it so the macrophages can’t eat the bacteria, which is bad,' said Zeldin.
Edin added that some researchers have tested sEH inhibitors — compounds that prevent sEH from degrading EETs — in clinical trials to see whether they could help with pain, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, and high blood pressure. He cautioned that the scientists performing these studies consider the influence of sEH inhibitors on bacterial clearance.
'They should be careful and stop using them if the individual develops pneumonia,' said Edin. 'Our study demonstrated that blocking sEH means EETs may hamstring macrophages, making a lung infection worse.'
 Garantziotis is also head of the NIEHS Matrix Biology Group. (Photo courtesy of Steve McCaw / NIEHS)
Garantziotis is also head of the NIEHS Matrix Biology Group. (Photo courtesy of Steve McCaw / NIEHS)Co-author Stavros Garantziotis, M.D., medical director of the NIEHS Clinical Research Unit, was instrumental in collecting human macrophages for the research.
'Since our study utilized lung immune cells from healthy volunteers, we have confidence that our findings are relevant to human health,' said Garantziotis.
Citation: Li H, Bradbury JA, Edin ML, Graves JP, Gruzdev A, Cheng J, Hoopes SL, DeGraff LM, Fessler MB, Garantziotis S, Schurman SH, Zeldin DC. 2021. sEH promotes macrophage phagocytosis and lung clearance of Streptococcus pneumoniae. J Clin Invest 131(22):e129679.









